C#动态编译
现在写的项目涉及了在.net standard下的动态编译,这篇文章就是来记录一下实现动态编译的过程。
CodeDom
一开始我使用的是System.CodeDom,在运行时会报错提示平台不支持的错误,在查询后发现.Net Standard不支持System.CodeDom,需要在上面一层建立和Roslyn依赖关系。Roslyn是一种.net 编译器。这一层也有人提供,叫Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform。但我这次的实现并没有用到这个。
用Roslyn实现动态编译
比起绕来绕去,就干脆直接用Roslyn实现感觉会更有效率。 需要的nuget包:
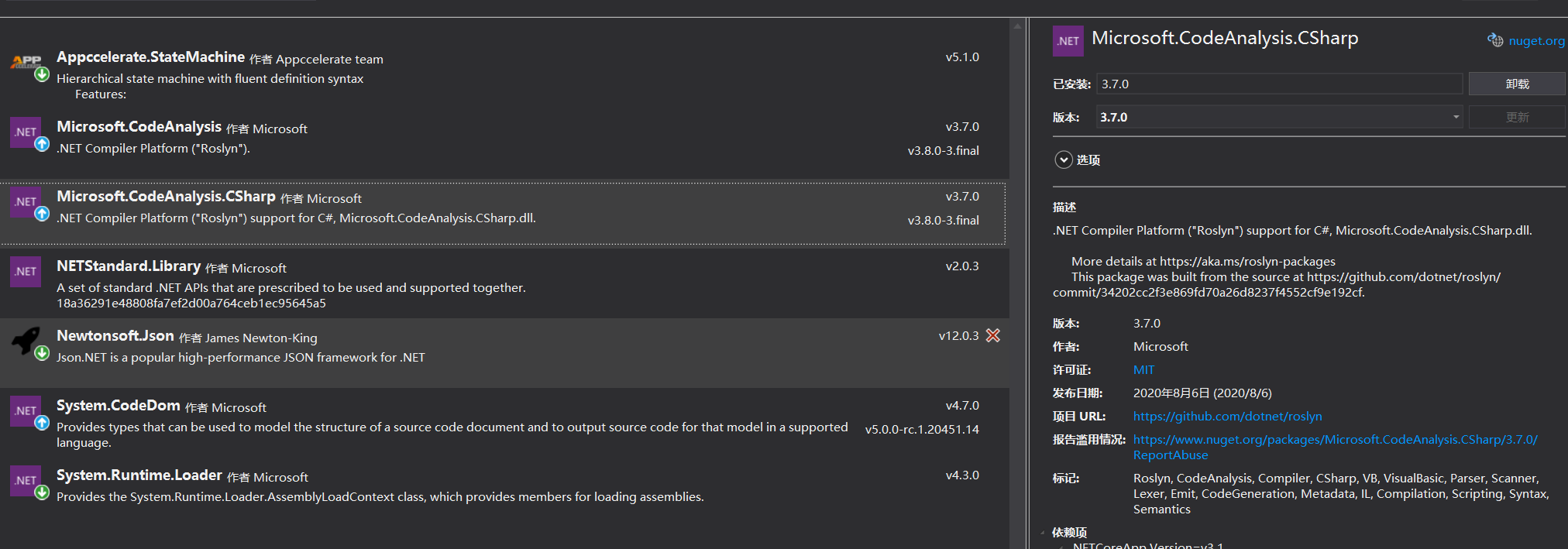
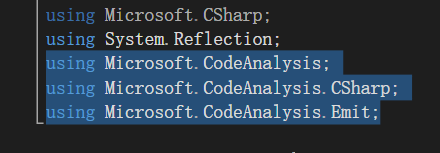
整个动态编译的过程如下:
- 获取需要编译的完整代码 我的代码的内容主要是提供一个判断转换条件,给出转换结果的函数。这里给出一个测试案例对应生成的动态代码。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Transitions
{
public class GetTransitions
{
public string getTransition(params object[] Parameters)
{
Dictionary<string, object> AliasValue = Parameters[0] as Dictionary<string, object>;
int stateNo = (int)Parameters[1];
System.Int32? numA = AliasValue["numA"] as System.Int32?;
System.Int32? numB = AliasValue["numB"] as System.Int32?;
System.Int32? numC = AliasValue["numC"] as System.Int32?;
System.String strD = AliasValue["strD"] as System.String;
switch(stateNo)
{
case 0:
if(numA >10){ return "goB";}
if(numA<=10){ return "goC";}
else{ return "Default";}
case 1:
if(numB>10){ return "goD";}
else{ return "Default";}
case 2:if(numC>10){ return "goD";}
else{ return "Default";}
case 3:if(strD == "end")
{ return "goA";}
else{ return "Default";}
default: return null;
}
}
}
}
- 获取代码分析得到的语法树
var syntaxTree = SyntaxFactory.ParseSyntaxTree(dynamicCode);
- 加载MetadataReference
MetadataReference[] references = new MetadataReference[]
{
MetadataReference.CreateFromFile(typeof(object).Assembly.Location),
MetadataReference.CreateFromFile(typeof(Enumerable).Assembly.Location)
};
- 创建编译任务
CSharpCompilation compilation = CSharpCompilation.Create(
assenmblyName, //指定程序集名称
syntaxTrees: new[] { syntaxTree }, //获取代码树
references: references, //添加程序集引用
options: new CSharpCompilationOptions(OutputKind.DynamicallyLinkedLibrary)); //输出为dll程序集
- 将IL代码写进内存
EmitResult result = compilation.Emit(ms);
if (!result.Success) //判断编译是否成功
{
// handle exceptions
IEnumerable<Diagnostic> failures = result.Diagnostics.Where(diagnostic =>
diagnostic.IsWarningAsError ||
diagnostic.Severity == DiagnosticSeverity.Error);
foreach (Diagnostic diagnostic in failures)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("{0}: {1}", diagnostic.Id, diagnostic.GetMessage());
}
}
成功了话到这里编译差不多结束,接着就是引用动态代码里的方法
- 获取程序集对象
else
{
// load this 'virtual' DLL so that we can use
ms.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
Assembly objAssembly = Assembly.Load(ms.ToArray());
// create instance of the desired class and call the desired function
typeDynamicAssenmbly = objAssembly.GetType("Transitions.GetTransitions");
objDynamicAssenmbly = Activator.CreateInstance(typeDynamicAssenmbly);
}
- 调用方法
var codeParams = new object[] { aliasValue, StatesConfig.CurrentState };
string result = typeDynamicAssenmbly.InvokeMember("getTransition",
BindingFlags.Default | BindingFlags.InvokeMethod,
null,
objDynamicAssenmbly,
codeParams) as string;
动态编译部分完整代码:
private static readonly IEnumerable<string> DefaultNamespaces =new[]
{
"System",
"System.IO",
"System.Net",
"System.Linq",
"System.Text",
"System.Text.RegularExpressions",
"System.Collections.Generic"
};
public void DynamicCompile(string dynamicCode)
{
if (dynamicCode!=null)
{
try
{
var syntaxTree = SyntaxFactory.ParseSyntaxTree(dynamicCode);
MetadataReference[] references = new MetadataReference[]
{
MetadataReference.CreateFromFile(typeof(object).Assembly.Location),
MetadataReference.CreateFromFile(typeof(Enumerable).Assembly.Location)
};
string assenmblyName = "Transitions";
CSharpCompilation compilation = CSharpCompilation.Create(
assenmblyName,
syntaxTrees: new[] { syntaxTree },
references: references,
options: new CSharpCompilationOptions(OutputKind.DynamicallyLinkedLibrary));
using (var ms = new MemoryStream())
{
// write IL code into memory
EmitResult result = compilation.Emit(ms);
if (!result.Success)
{
// handle exceptions
IEnumerable<Diagnostic> failures = result.Diagnostics.Where(diagnostic =>
diagnostic.IsWarningAsError ||
diagnostic.Severity == DiagnosticSeverity.Error);
foreach (Diagnostic diagnostic in failures)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("{0}: {1}", diagnostic.Id, diagnostic.GetMessage());
}
}
else
{
// load this 'virtual' DLL so that we can use
ms.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
Assembly objAssembly = Assembly.Load(ms.ToArray());
// create instance of the desired class and call the desired function
typeDynamicAssenmbly = objAssembly.GetType("Transitions.GetTransitions");
objDynamicAssenmbly = Activator.CreateInstance(typeDynamicAssenmbly);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("DynamicCode is null!");
}
}
这样就是.net standard中动态编译的全过程了
本文章使用limfx的vsocde插件快速发布