面向对象编程(中级部分)
包
一个项目中不能有两个同名的类,因此引出了包的概念
包的三大作用:
- 区分相同名字的类
- 当类很多时,可以很好的管理类[看Java API文档]
- 控制访问范围
包基本语法:
package com.util;
说明:
- package:关键字,表示打包
- com.util:表示包名
包的本质分析(原理):
包的本质实际上就是创建不同的文件夹/目录来保存类文件
包的命名:
命名规则:
只能包含数字、字母、下划线、小圆点..但不能用数字开头,不能是关键字或保留字
demo.class.exec1//错误 class是关键字
demo.12a//错误12a是数字开头
demo.ab12.oa//对
命名规范:
一般是小写字母+小圆点一般是com.公司名.项目名.业务模块名
举例:
com.sina.crm.user//用户模块
com.sina.crm.order/订单模块
com.sina.crm.utils //工具类
常用的包:
一个包下,包含很多的类,Java 中常用的包有:
- java.lang.* //lang 包是基本包,默认引入,不需要再引入
- java.util.* //util 包,系统提供的工具包, 工具类,使用 Scanner
- java.net.* //网络包,网络开发
- java.awt.* //是做 java 的界面开发,GUI
用什么类就引用什么类,尽量不用*的形式
注意事项和使用细节:
- package的作用是声明当前类所在的包,需要放在类的最上面,一个类中最多只有一句package
- import指令位置放在package的下面,在类定义前面,可以有多句且没有顺序要求。
访问修饰符
基本介绍: Java 提供四种访问控制修饰符号,用于控制方法和属性(成员变量)的访问权限(范围):
- 公开级别:用 public 修饰,对外公开
- 受保护级别:用 protected 修饰,对子类和同一个包中的类公开
- 默认级别:没有修饰符号,向同一个包的类公开
- 私有级别:用 private 修饰,只有类本身可以访问,不对外公开
访问修饰符的访问范围
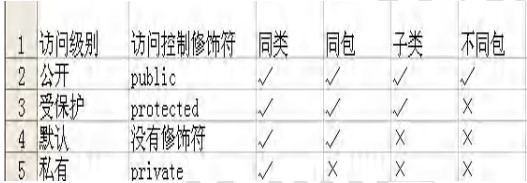
1)修饰符可以用来修饰类中的属性,成员方法以及类
2)只有默认的和public才能修饰类!,并且遵循上述访问权限的特点
3)成员方法的访问规则和属性完全一样
面向对象编程三大特征:封装、继承和多态
封装
封装(encapsulation)就是把抽象出的数据[属性]和对数据的操作[方法]封装在一起,数据被保护在内部,程序的其它部分只有通过被授权的操作[方法],才能对数据进行操作。
封装的理解和好处
1)隐藏实现细节:方法(连接数据库)<--调用(传入参数..)
2)可以对数据进行验证,保证安全合理
Person {name, age}
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "jack"” ;
p.age = 1200;//未对数据进行验证
封装的实现步骤(三步)
1)将属性进行私有化private【不能直接修改属性】
2)提供一个公共的(public)set方法,用于对属性判断并赋值
public void setXxx(类型参数名){//Xxx表示某个属性
//加入数据验证的业务逻辑
属性=参数名;
}
3)提供一个公共的(public)get方法,用于获取属性的值
public 数据类型 getXxx(){//权限判断,Xxx某个属性
return xx;
}
入门案例:
请大家看一个小程序,不能随便查看人的年龄,工资等隐私,并对设置的年龄进行合理的验证。年龄合理就设置,否则给默认年龄,必须在1-120,年龄,工资不能直接查看,
name的长度在2-6字符之间。
package com.fyx.encap;
public class Encapsulation01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("jack");
person.setAge(300);
person.setSalary(30000);
System.out.println(person.info());
}
}
/*
不能随便查看人的年龄,工资等隐私,并对设置的年龄进行合理的验证。年龄合理就设置,否则给默认
年龄, 必须在 1-120, 年龄, 工资不能直接查看 , name的长度在 2-6字符 之间
*/
class Person{
public String name; //名字公开
private int age; //age 私有化
private double salary; //..
//自己写setXxx 和 getXxx 太慢,我们使用快捷键
//然后根据要求来完善我们的代码
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
//加入对数据的校验,相当于增加了业务逻辑
if(name.length() >= 2 && name.length() <=6 ) {
this.name = name;
}else {
System.out.println("名字的长度不对,需要(2-6)个字符,默认名字");
this.name = "无名人";
}
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
//判断
if(age >= 1 && age <= 120) {//如果是合理范围
this.age = age;
} else {
System.out.println("你设置年龄不对,需要在 (1-120), 给默认年龄18 ");
this.age = 18;//给一个默认年龄
}
}
public double getSalary() {
//可以这里增加对当前对象的权限判断
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//写一个方法,返回属性信息
public String info() {
return "信息为 name=" + name + " age=" + age + " 薪水=" + salary;
}
}
创建程序,在其中定义两个类:Account 和 AccountTest 类体会 Java 的封装性。
- Account 类要求具有属性:姓名(长度为 2 位 3 位或 4 位)、余额(必须>20)、
- 密码(必须是六位), 如果不满足,则给出提示信息,并给默认值(程序员自己定)
- 通过 setXxx 的方法给 Account 的属性赋值。
- 在 AccountTest 中测试
package com.fyx.encap;
/*
* 创建程序,在其中定义两个类:Account和AccountTest类体会Java的封装性。
* Account类要求具有属性:姓名(长度为2位3位或4位)、余额(必须>20)、
* 密码(必须是六位), 如果不满足,则给出提示信息,并给默认值(程序员自己定)
* 通过setXxx的方法给Account 的属性赋值。
* 在AccountTest中测试
*/
public class Account {
//为了封装,将3个属性设置为private
private String name;
private double balance;
private String pwd;
//提供两个构造器
public Account() {
}
public Account(String name, double balance, String pwd) {
this.setName(name);
this.setBalance(balance);
this.setPwd(pwd);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
//姓名(长度为2位3位或4位)
public void setName(String name) {
if (name.length() >= 2 && name.length() <= 4) {
this.name = name;
} else {
System.out.println("姓名要求(长度为2位3位或4位),默认值 无名");
this.name = "无名";
}
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
if (balance > 20) {
this.balance = balance;
} else {
System.out.println("余额(必须>20) 默认为0");
}
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
//密码(必须是六位)
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
if (pwd.length() == 6) {
this.pwd = pwd;
} else {
System.out.println("密码(必须是六位)默认密码为 000000");
this.pwd = "000000";
}
}
//显示账号信息
public void showInfo() {
//可以增加权限的校验
System.out.println("账号信息 name=" + name + " 余额=" + balance + " 密码" + pwd);
// if() {
// System.out.println("账号信息 name=" + name + " 余额=" + balance + " 密码");
// }else{
// System.out.println("你无权查看...");
// }
}
}
package com.fyx.encap;
public class AccountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Account
Account account = new Account();
account.setName("jack");
account.setBalance(600);
account.setPwd("123456");
account.showInfo();
}
}
继承
我们编写了两个类,一个是Pupil类(小学生),一个是Graduate(大学毕业生)。问题:两个类的属性和方法有很多是相同的,怎么办? =>继承(代码复用性~)
继承基本介绍和示意图
继承可以解决代码复用,让我们的编程更加靠近人类思维。当多个类存在相同的属性(变量)和方法时,可以从这些类中抽象出父类,在父类中定义这些相同的属性和方法,所有的子类不需要重新定义这些属性和方法,只需要通过 extends 来声明继承父类即可。画出继承的示意图

继承的基本语法
class子类extends父类{
}
1)子类就会自动拥有父类定义的属性和方法
2)父类又叫超类,基类。
3)子类又叫派生类。
继承给编程带来的便利
1)代码的复用性提高了
2)代码的扩展性和维护性提高了
继承的深入讨论/细节问题
- 子类继承了所有的属性和方法,非私有的属性和方法可以在子类直接访问, 但是私有属性和方法不能在子类直接访问,要通过父类提供公共的方法去访问
- 子类必须调用父类的构造器, 完成父类的初始化
- 当创建子类对象时,不管使用子类的哪个构造器,默认情况下总会去调用父类的无参构造器,如果父类没有提供无参构造器,则必须在子类的构造器中用 super 去指定使用父类的哪个构造器完成对父类的初始化工作,否则,编译不会通过
- 如果希望指定去调用父类的某个构造器,则显式的调用一下 : super(参数列表)
- super 在使用时,必须放在构造器第一行(super 只能在构造器中使用)
- super() 和 this() 都只能放在构造器第一行,因此这两个方法不能共存在一个构造器
- Java 所有类都是 Object 类的子类, Object 是所有类的基类
- 父类构造器的调用不限于直接父类!将一直往上追溯直到 Object 类(顶级父类)
- 子类最多只能继承一个父类(指直接继承),即 Java 中是单继承机制。
- 不能滥用继承,子类和父类之间必须满足 is-a 的逻辑关系
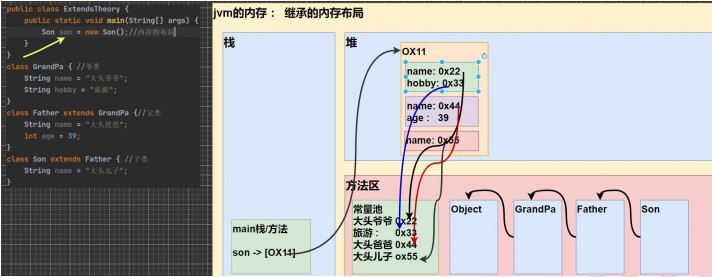
继承的本质分析
练习
- 观察输出结果
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
public class ExtendsExercise01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b=new B();//a , b name, b
}
}
class A {
A() {
System.out.println("a");
}
A(String name) {
System.out.println("a name");
}
}
class B extends A {
B() {
this("abc");
System.out.println("b");
}
B(String name) {
//默认有 super();去调用A的无参构造器
System.out.println("b name");
}
}
- 观察输出结果
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
public class ExtendsExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C c = new C();
}
}
class A {//A类
public A() {
System.out.println("我是A类");
}
}
class B extends A { //B类,继承A类 //main方法中: C c =new C(); 输出么内容? 3min
public B() {
System.out.println("我是B类的无参构造");
}
public B(String name) {
System.out.println(name + "我是B类的有参构造");
}
}
class C extends B { //C类,继承 B类
public C() {
this("hello");
System.out.println("我是c类的无参构造");
}
public C(String name) {
super("haha");
System.out.println("我是c类的有参构造");
}
}
- 编写 Computer 类,包含 CPU、内存、硬盘等属性,getDetails 方法用于返回 Computer 的详细信息
编写 PC 子类,继承 Computer 类,添加特有属性【品牌 brand】
编写 NotePad 子类,继承 Computer 类,添加特有属性【color】
编写 Test 类,在 main 方法中创建 PC 和 NotePad 对象,分别给对象中特有的属性赋值,以及从 Computer 类继承的属性赋值,并使用方法并打印输出信息
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
public class ExtendsExercise03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PC pc = new PC("intel", 16, 500, "IBM");
pc.printInfo();
NotePad notePad = new NotePad("iPad",16,200,"暗夜紫");
notePad.printInfo();
}
}
/*
编写Computer类,包含CPU、内存、硬盘等属性,getDetails方法用于返回Computer的详细信息
编写PC子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【品牌brand】
编写NotePad子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【color】
编写Test类,在main方法中创建PC和NotePad对象,分别给对象中特有的属性赋值,
以及从Computer类继承的属性赋值,并使用方法并打印输出信息
*/
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
//编写Computer类,包含CPU、内存、硬盘等属性,getDetails方法用于返回Computer的详细信息
public class Computer {
private String cpu;
private int memory;
private int disk;
public Computer(String cpu, int memory, int disk) {
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.disk = disk;
}
//返回Computer信息
public String getDetails() {
return "cpu=" + cpu + " memory=" + memory + " disk=" + disk;
}
public String getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public void setCpu(String cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public int getMemory() {
return memory;
}
public void setMemory(int memory) {
this.memory = memory;
}
public int getDisk() {
return disk;
}
public void setDisk(int disk) {
this.disk = disk;
}
}
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
//编写PC子类,继承Computer类,添加特有属性【品牌brand】
public class PC extends Computer {
private String brand;
//这里IDEA 根据继承的规则,自动把构造器的调用写好
//这里也体现: 继承设计的基本思想,父类的构造器完成父类属性初始化
//子类的构造器完成子类属性初始化
public PC(String cpu, int memory, int disk, String brand) {
super(cpu, memory, disk);
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("PC信息=");
//System.out.println(getCpu() + getMemory() + getDisk());
//调用父类的getDetails方法,得到相关属性信息...
System.out.println(getDetails() + " brand=" + brand);
}
}
package com.fyx.extend_.exercise;
public class NotePad extends Computer{
private String color;
public NotePad(String cpu, int memory, int disk, String color) {
super(cpu, memory, disk);
this.color = color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("NotePad信息=");
System.out.println(getDetails() + " color=" + color);
}
}
super关键字
super 代表父类的引用,用于访问父类的属性、方法、构造器
基本语法:
- 访问父类的属性,但不能访问父类的private属性 super.属性名;
- 访问父类的方法,不能访问父类的private方法 super.方法名(参数列表);
- 访问父类的构造器: super(参数列表);只能放在构造器的第一句,只能出现一句!
super 给编程带来的便利/细节:
- 调用父类的构造器的好处(分工明确,父类属性由父类初始化,子类的属性由子类初始化)
- 当子类中有和父类中的成员(属性和方法)重名时,为了访问父类的成员,必须通过super。如果没有重名,使用super、this、直接访问是一样的效果!
- super的访问不限于直接父类,如果爷爷类和本类中有同名的成员,也可以使用super去访问爷爷类的成员;如果多个基类(上级类)中都有同名的成员,使用super访问遵循就近原则。A->B->C,当然也需要遵守访问权限的相关规则
super 和 this 的比较

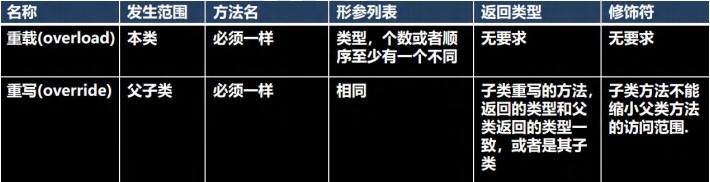
方法重写/覆盖(override)
简单的说:方法覆盖(重写)就是子类有一个方法,和父类的某个方法的名称、返回类型、参数一样,那么我们就说子类的这个方法覆盖了父类的方法
注意事项和使用细节:
方法重写也叫方法覆盖,需要满足下面的条件
- 子类的方法的形参列表,方法名称,要和父类方法的形参列表,方法名称完全一样。
- 子类方法的返回类型和父类方法返回类型一样,或者是父类返回类型的子类比如父类返回类型是Object,子类方法返回类型是String
- 子类方法不能缩小父类方法的访问权限 public > protected >默认>private
重写与重载比较
练习
编写一个 Person 类,包括属性/private(name、age),构造器、方法 say(返回自我介绍的字符串)。 编写一个 Student 类,继承 Person 类,增加 id、score 属性/private,以及构造器,定义 say 方法(返回自我介绍的信息)。 在 main 中,分别创建 Person 和 Student 对象,调用 say 方法输出自我介绍
package com.fyx.override_;
public class OverrideExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在main中,分别创建Person和Student对象,调用say方法输出自我介绍
Person jack = new Person("jack", 10);
System.out.println(jack.say());
Student smith = new Student("smith", 20, 123456, 99.8);
System.out.println(smith.say());
}
}
package com.fyx.override_;
//编写一个Person类,包括属性/private(name、age),构造器、方法say(返回自我介绍的字符串)
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String say() {
return "name=" + name + " age=" + age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.fyx.override_;
//编写一个Student类,继承Person类,增加id、score属性/private,以及构造器,定义say方法(返回自我介绍的信息)。
public class Student extends Person{
private int id;
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age, int id, double score) {
super(name, age);//这里会调用父类构造器
this.id = id;
this.score = score;
}
//say
public String say() { //这里体现super的一个好处,代码复用.
return super.say() + " id=" + id + " score=" + score;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
多态
方法或对象具有多种形态。是面向对象的第三大特征,多态是建立在封装和继承基础之上的。
多态的具体体现
- 方法的多态
重写和重载就体现多态
package com.fyx.poly_;
public class PloyMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法重载体现多态
A a = new A();
//这里我们传入不同的参数,就会调用不同sum方法,就体现多态
System.out.println(a.sum(10, 20));
System.out.println(a.sum(10, 20, 30));
//方法重写体现多态
B b = new B();
a.say();
b.say();
}
}
class B { //父类
public void say() {
System.out.println("B say() 方法被调用...");
}
}
class A extends B {//子类
public int sum(int n1, int n2){//和下面sum 构成重载
return n1 + n2;
}
public int sum(int n1, int n2, int n3){
return n1 + n2 + n3;
}
public void say() {
System.out.println("A say() 方法被调用...");
}
}
- 对象的多态 (核心,困难,重点)
重要的几句话(记住): (1)一个对象的编译类型和运行类型可以不一致
(2)编译类型在定义对象时,就确定了,不能改变
(3)运行类型是可以变化的
(4)编译类型看定义时=号的左边,运行类型看=号的右边
package com.fyx.poly_.objectpoly_;
public class Animal {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("Animal cry() 动物在叫....");
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.objectpoly_;
public class Cat extends Animal{
public void cry() {
System.out.println("Cat cry() 小猫喵喵叫...");
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.objectpoly_;
public class Dog extends Animal {
public void cry() {
System.out.println("Dog cry() 小狗汪汪叫...");
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.objectpoly_;
public class PolyObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//体验对象多态特点
//animal 编译类型就是 Animal , 运行类型 Dog
Animal animal = new Dog();
//因为运行时 , 执行到该行时,animal运行类型是Dog,所以cry就是Dog的cry
animal.cry(); //小狗汪汪叫
//animal 编译类型 Animal,运行类型就是 Cat
animal = new Cat();
animal.cry(); //小猫喵喵叫
}
}
多态注意事项和细节讨论
多态的前提是:两个对象(类)存在继承关系
(1)多态的向上转型
- 本质:父类的引用指向了子类的对象
- 语法:父类类型 引用名=new 子类类型();
- 特点:编译类型看左边,运行类型看右边。
可以调用父类中的所有成员(需遵守访问权限), 不能调用子类中特有成员;
最终运行效果看子类的具体实现!
(2)多态向下转型
- 语法:子类类型 引用名=(子类类型) 父类引用;
- 只能强转父类的引用,不能强转父类的对象
- 要求父类的引用必须指向的是当前目标类型的对象
- 当向下转型后,可以调用子类类型中所有的成员
(3)属性没有重写之说!属性的值看编译类型
(4)instanceOf 比较操作符,用于判断对象的运行类型是否为 XX 类型或 XX 类型的子类型
练习


Java动态绑定机制(非常非常重要)
Java的动态绑定机制
- 当调用对象方法的时候,该方法会和该对象的内存地址/运行类型绑定
- 当调用对象属性时,没有动态绑定机制,哪里声明,那里使用
package com.fyx.poly_.dynamic_;
public class DynamicBinding {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//a 的编译类型 A, 运行类型 B
A a = new B();//向上转型
System.out.println(a.sum());//?40 -> 30
System.out.println(a.sum1());//?30-> 20
}
}
class A {//父类
public int i = 10;
//动态绑定机制:
public int sum() {//父类sum()
return getI() + 10;//20 + 10
}
public int sum1() {//父类sum1()
return i + 10;//10 + 10
}
public int getI() {//父类getI
return i;
}
}
class B extends A {//子类
public int i = 20;
// public int sum() {
// return i + 20;
// }
public int getI() {//子类getI()
return i;
}
// public int sum1() {
// return i + 10;
// }
}
多态的应用
- 多态数组
数组的定义类型为父类类型,里面保存的实际元素类型为子类类型
应用实例:现有一个继承结构如下:要求创建 1 个 Person 对象、2 个 Student 对象和 2 个 Teacher 对象, 统一放在数组
中,并调用每个对象say 方法
应用实例升级:如何调用子类特有的方法,比如Teacher 有一个 teach , Student 有一个 study 怎么调用?
package com.fyx.poly_.polyarr_;
public class Person {//父类
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String say() {//返回名字和年龄
return name + "\t" + age;
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyarr_;
public class Student extends Person {
private double score;
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
//重写父类say
@Override
public String say() {
return "学生 " + super.say() + " score=" + score;
}
//特有的方法
public void study() {
System.out.println("学生 " + getName() + " 正在学java...");
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyarr_;
public class Teacher extends Person {
private double salary;
public Teacher(String name, int age, double salary) {
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//写重写父类的say方法
@Override
public String say() {
return "老师 " + super.say() + " salary=" + salary;
}
//特有方法
public void teach() {
System.out.println("老师 " + getName() + " 正在讲java课程...");
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyarr_;
public class PloyArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//应用实例:现有一个继承结构如下:要求创建1个Person对象、
// 2个Student 对象和2个Teacher对象, 统一放在数组中,并调用每个对象say方法
Person[] persons = new Person[5];
persons[0] = new Person("jack", 20);
persons[1] = new Student("mary", 18, 100);
persons[2] = new Student("smith", 19, 30.1);
persons[3] = new Teacher("scott", 30, 20000);
persons[4] = new Teacher("king", 50, 25000);
//循环遍历多态数组,调用say
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
//老师提示: person[i] 编译类型是 Person ,运行类型是是根据实际情况有JVM来判断
System.out.println(persons[i].say());//动态绑定机制
//使用 类型判断 + 向下转型.
if(persons[i] instanceof Student) {//判断person[i] 的运行类型是不是Student
Student student = (Student)persons[i];//向下转型
student.study();
//也可以使用一条语句 ((Student)persons[i]).study();
} else if(persons[i] instanceof Teacher) {
Teacher teacher = (Teacher)persons[i];
teacher.teach();
} else if(persons[i] instanceof Person){
//System.out.println("你的类型有误, 请自己检查...");
} else {
System.out.println("你的类型有误, 请自己检查...");
}
}
}
}
- 多态参数
方法定义的形参类型为父类类型,实参类型允许为子类类型
定义员工类Employee,包含姓名和月工资[private],以及计算年工资getAnnual的方法。普通员工和经理继承了员工,经理类多了奖金bonus属性和管理manage方法,普通员工类多了work方法,普通员工和经理类要求分别重写getAnnual方法
测试类中添加一个方法showEmpAnnual(Employee e),实现获取任何员工对象的年工资,并在main方法中调用该方法[e.getAnnual0]
测试类中添加一个方法,testWork,如果是普通员工,则调用work方法,如果是经理,则调用manage方法
package com.fyx.poly_.polyparameter_;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String name, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
//得到年工资的方法
public double getAnnual() {
return 12 * getSalary();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyparameter_;
public class Worker extends Employee {
public Worker(String name, double salary) {
super(name, salary);
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("普通员工 " + getName() + " is working");
}
@Override
public double getAnnual() {//因为普通员工没有其它收入,则直接调用父类方法
return super.getAnnual();
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyparameter_;
public class Manager extends Employee{
private double bonus;
public Manager(String name, double salary, double bonus) {
super(name, salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public void manage() {
System.out.println("经理 " + getName() + " is managing");
}
//重写获取年薪方法
@Override
public double getAnnual() {
return super.getAnnual() + bonus;
}
}
package com.fyx.poly_.polyparameter_;
public class PloyParameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker tom = new Worker("tom", 2500);
Manager milan = new Manager("milan", 5000, 200000);
PloyParameter ployParameter = new PloyParameter();
ployParameter.showEmpAnnual(tom);
ployParameter.showEmpAnnual(milan);
ployParameter.testWork(tom);
ployParameter.testWork(milan);
}
//showEmpAnnual(Employee e)
//实现获取任何员工对象的年工资,并在main方法中调用该方法 [e.getAnnual()]
public void showEmpAnnual(Employee e) {
System.out.println(e.getAnnual());//动态绑定机制.
}
//添加一个方法,testWork,如果是普通员工,则调用work方法,如果是经理,则调用manage方法
public void testWork(Employee e) {
if(e instanceof Worker) {
((Worker) e).work();//有向下转型操作
} else if(e instanceof Manager) {
((Manager) e).manage();//有向下转型操作
} else {
System.out.println("不做处理...");
}
}
}
Object 类详解
equals 方法
==和equals的对比[面试题]
==是一个比较运算符
- ==:既可以判断基本类型,又可以判断引用类型
- ==:如果判断基本类型,判断的是值是否相等。示例: int i=10; double d=10.0;
- ==:如果判断引用类型,判断的是地址是否相等,即判定是不是同一个对象
- equals:是Object类中的方法,只能判断引用类型,如何看Jdk源码
- 默认判断的是地址是否相等,子类中往往重写该方法,用于判断内容是否相等。比如Integer,String【看看String 和Integer的 equals源代码】
如何重写 equals 方法
应用实例: 判断两个 Person 对象的内容是否相等,如果两个 Person 对象的各个属性值都一样,则返回 true,反之 false。
package com.fyx.object_;
public class EqualsExercise01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person1 = new Person("jack", 10, '男');
Person person2 = new Person("jack", 20, '男');
System.out.println(person1.equals(person2));//假
}
}
//判断两个Person对象的内容是否相等,
//如果两个Person对象的各个属性值都一样,则返回true,反之false
class Person { //extends Object
private String name;
private int age;
private char gender;
//重写Object 的 equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj){
//判断如果比较的两个对象是同一个对象,则直接返回true
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
//类型判断
if(obj instanceof Person) {//是Person,我们才比较
//进行 向下转型, 因为我需要得到obj的 各个属性
Person p = (Person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age && this.gender == p.gender;
}
return false;
}
public Person(String name, int age, char gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
}
hashCode 方法
小结:
- 提高具有哈希结构的容器的效率!
- 两个引用,如果指向的是同一个对象,则哈希值肯定是一样的!
- 两个引用,如果指向的是不同对象,则哈希值是不一样的
- 哈希值主要根据地址号来的!, 不能完全将哈希值等价于地址。
toString 方法
- 基本介绍 默认返回:全类名+@+哈希值的十六进制,【查看 Object 的 toString 方法】 子类往往重写 toString 方法,用于返回对象的属性信息
- 重写 toString 方法,打印对象或拼接对象时,都会自动调用该对象的 toString 形式.
- 当直接输出一个对象时,toString 方法会被默认的调用,比如 System.out.println(monster); 就会默认调用monster.toString()
package com.fyx.object_;
public class ToString_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Object的toString() 源码
(1)getClass().getName() 类的全类名(包名+类名 )
(2)Integer.toHexString(hashCode()) 将对象的hashCode值转成16进制字符串
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
*/
Monster monster = new Monster("小妖怪", "巡山的", 1000);
System.out.println(monster.toString() + " hashcode=" + monster.hashCode());
System.out.println("==当直接输出一个对象时,toString 方法会被默认的调用==");
System.out.println(monster); //等价 monster.toString()
}
}
class Monster {
private String name;
private String job;
private double sal;
public Monster(String name, String job, double sal) {
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
this.sal = sal;
}
//重写toString方法, 输出对象的属性
//使用快捷键即可 alt+insert -> toString
@Override
public String toString() {//重写后,一般是把对象的属性值输出,当然程序员也可以自己定制
return "Monster{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
'}';
}
}
finalize 方法
- 当对象被回收时,系统自动调用该对象的 finalize 方法。子类可以重写该方法,做一些释放资源的操作
- 什么时候被回收:当某个对象没有任何引用时,则 jvm 就认为这个对象是一个垃圾对象,就会使用垃圾回收机制来销毁该对象,在销毁该对象前,会先调用 finalize 方法。
- 垃圾回收机制的调用,是由系统来决定(即有自己的 GC 算法), 也可以通过 System.gc() 主动触发垃圾回收机制,测 试:Car [name]
提示: 我们在实际开发中,几乎不会运用 finalize , 所以更多就是为了应付面试
package com.fyx.object_;
public class Finalize_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car bmw = new Car("宝马");
bmw = null;
//这时 car对象就是一个垃圾,垃圾回收器就会回收(销毁)对象
//,在销毁对象前,会调用该对象的finalize方法
//,程序员就可以在 finalize中,写自己的业务逻辑代码(比如释放资源:数据库连接,或者打开文件..)
//,如果程序员不重写 finalize,那么就会调用 Object类的 finalize, 即默认处理
//,如果程序员重写了finalize, 就可以实现自己的逻辑
System.gc();//主动调用垃圾回收器
System.out.println("程序退出了....");
}
}
class Car {
private String name;
//属性, 资源。。
public Car(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//重写finalize
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println("我们销毁 汽车" + name );
System.out.println("释放了某些资源...");
}
}
断点调试(debug)
重要提示:
在断点调试过程中,是运行状态,是以对象的运行类型来执行的
- 断点调试是指在程序的某一行设置一个断点,调试时,程序运行到这一行就会停住,然后你可以一步一步往下调试,调试过程中可以看各个变量当前的值,出错的话,调试到出错的代码行即显示错误,停下。进行分析从而找到这个Bug
- 断点调试是程序员必须掌握的技能。
- 断点调试也能帮助我们查看java底层源代码的执行过程,提高程序员的Java水平。
断点调试的快捷键:(笔记本需加上fn键一起按)
F7(跳入)
F8(跳过)
shift+F8(跳出)
F9(resume,执行到下一个断点)
F7:跳入方法内
F8: 逐行执行代码
shift+F8: 跳出方法
断点可以在 debug 过程中,动态地下断点
作业
- 定义一个Person类 {name, age, job}, 初始化Person 对象数组,有3个person对象,并按照 age 从 大到 小进行排序, 提示,使用冒泡排序
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] persons = new Person[3];
persons[0] = new Person("mary",30, "PHP工程师");
persons[1] = new Person("tom",50, "大数据工程师");
persons[2] = new Person("smith",10, "JavaEE工程师");
//输出当前对象数组
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
System.out.println(persons[i]);//默认对象的.toString()
}
//使用冒泡排序
Person tmp = null;//临时变量,用于交换
for(int i = 0; i < persons.length -1 ;i++) {//外层循环
for(int j = 0; j < persons.length -1 - i; j++) {//内层循环
//并按照 age 从 大到 小进行排序, 如果前面的人的age < 后面人的年龄,就交换
//要求按照名字的长度从小到大 if(persons[i].getName().length() > persons[i+1].getName().length())
if(persons[j].getAge() < persons[j+1].getAge()) {
tmp = persons[j];
persons[j] = persons[j+1];
persons[j+1]= tmp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("=================排序后的效果================");
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
System.out.println(persons[i]);//默认对象的.toString()
}
}
}
/*
定义一个Person类 {name, age, job}, 初始化Person 对象数组,有3个person对象,
并按照 age 从 大到 小进行排序, 提示,使用冒泡排序
*/
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
private String job;
public Person(String name, int age, String job) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
-
编写老师类(1)要求有属性“姓名name”,“年龄age”,“职称post",“基本工资salary"
编写业务方法,introduce(),实现输出一个教师的信息。 编写教师类的三个子类:教授类(Professor )、副教授类、讲师类。工资级别分别为:教授为1.3、副教授为1.2、讲师类1.1。在三个子类里面都重写父类的introduce ()方法。 定义并初始化一个老师对象,调用业务方法,实现对象基本信息的后台打印 (只实现一个子类就行)
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Professor professor = new Professor("贾宝玉", 30, "高级职称", 30000, 1.3);
professor.introduce();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework;
/*
(1) 要求有属性“姓名name”,“年龄age”,“职称post”,“基本工资salary”
(2) 编写业务方法, introduce(),实现输出一个教师的信息。
*/
public class Teacher {
private String name;
private int age;
private String post;
private double salary;
//这里我们在增加一个工资级别
private double grade;
public Teacher(String name, int age, String post, double salary, double grade) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.post = post;
this.salary = salary;
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPost() {
return post;
}
public void setPost(String post) {
this.post = post;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(double grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public void introduce() {
System.out.println("name: " + name + " age: " + age
+ " post: " + post + " salary:" + salary + " grade:" + grade);
}
}
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Professor extends Teacher {
public Professor(String name, int age, String post, double salary, double grade) {
super(name, age, post, salary, grade);
}
@Override
public void introduce() {
System.out.println(" 这是教授的信息 ");
super.introduce();
}
}
- 通过继承实现员工工资核算打印功能 父类:员工类(Employee) 子类:部部门经理类(Manager)、普通员工类(Worker) (1)部门经理工资=1000+单日工资*天数*等级(1.2)。=>奖金+基本工资 (2)普通员工工资=单日工资*天数*等级(1.0) ; =>基本工资 (3)员工属性:姓名,单日工资,工作天数 (4)员工方法(打印工资) (5)普遍员工及部门经理都是员工子类,需要重写打印工资方法。 (6)定义并初始化普通员工对象,调用打印工资方法输出工资,定义并初始化部门经理对象,调用打印工资方法输出工资
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Homework03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Manager manage = new Manager("刘备", 500, 20, 1.2);
//设置奖金
manage.setBonus(1000);
//打印经理的工资情况
manage.printSal();
Worker worker = new Worker("关羽",100, 10, 1.0);
//打印员工的工资情况
worker.printSal();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Employee {
//属性
//员工属性:姓名,单日工资,工作天数
private String name;
private double daySal;
private int workDays;
//分析出还有一个属性等级
private double grade;
public Employee(String name, double daySal, int workDays, double grade) {
this.name = name;
this.daySal = daySal;
this.workDays = workDays;
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getDaySal() {
return daySal;
}
public void setDaySal(double daySal) {
this.daySal = daySal;
}
public int getWorkDays() {
return workDays;
}
public void setWorkDays(int workDays) {
this.workDays = workDays;
}
public double getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(double grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
//打印工资方法
//方法 void printSal() {}
public void printSal(){
System.out.println(name + " 工资=" + daySal * workDays * grade);
}
}
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Worker extends Employee{
public Worker(String name, double daySal, int workDays, double grade) {
super(name, daySal, workDays, grade);
}
//重写printSal
//因为普通员工和Employee输出工资情况一样,所以直接调用父类的printSal()
@Override
public void printSal() {
System.out.print("普通员工 ");//自己的输出信息
super.printSal();//调用父类的方法,复用代码
}
}
package com.fyx.homework;
public class Manager extends Employee{
//特有属性
private double bonus;
//创建Manager对象时,奖金是多少并不是确定的,因为在构造器中不给bonus,可以通过setBonus
public Manager(String name, double daySal, int workDays, double grade) {
super(name, daySal, workDays, grade);
}
//方法:重写父类的 printSal
@Override
public void printSal() {
//因为经理的工资计算方式和Employee不一样,所以重写
System.out.println("经理 " + getName() + " 工资是="
+ (bonus + getDaySal() * getWorkDays() * getGrade()));
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}
- 设计父类—员工类。子类:工人类(Worker),农民类(Peasant),教师类(Teacher),科学家类(Scientist),服务生类(Waiter). (1)其中工人,农民,服务生只有基本工资sal (2)教师除基本工资外,还有课酬(元/关) classDay, classSal (3)科学家除基本工资外,还有年终奖bonus (4)编写一个测试类,将各种类型的员工的全年工资打印出来
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Homework04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker jack = new Worker("jack", 10000);
jack.setSalMonth(15);//灵活额修改带薪月份
jack.printSal();
Peasant smith = new Peasant("smith", 20000);
smith.printSal();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter("mary",3000);
waiter.printSal();
//老师测试
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("milan", 2000);
//老师有课时费
teacher.setClassDays(360);
teacher.setClassSal(1000);
teacher.printSal();
//科学家
Scientist scientist = new Scientist("tony", 20000);
scientist.setBonus(2000000);
scientist.printSal();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Employee {
//属性
//分析有一个带薪的月份 13 , 15, 12
private String name;
private double sal;
private int salMonth = 12;
//方法
//打印全年工资
public void printSal() {
System.out.println(name + " 年工资是: " + (sal * salMonth));
}
public Employee(String name, double sal) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public int getSalMonth() {
return salMonth;
}
public void setSalMonth(int salMonth) {
this.salMonth = salMonth;
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Peasant extends Employee {
//子类
//属性
//农民,服务生只有基本工资 sal
//方法
public Peasant(String name, double sal) {
super(name, sal);
}
//年工资
@Override
public void printSal() {
System.out.print("农民 ");
super.printSal();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Scientist extends Employee{
//特有属性
//年终奖 bonus
private double bonus;
//方法
public Scientist(String name, double sal) {
super(name, sal);
}
//重写年工资打印
@Override
public void printSal() {
System.out.print("科学家 ");
System.out.println(getName() + " 年工资是: " + (getSal() * getSalMonth() + bonus));
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Waiter extends Employee{
public Waiter(String name, double sal) {
super(name, sal);
}
@Override
public void printSal() {
System.out.print("服务员 ");
super.printSal();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Worker extends Employee{//子类
//属性
//工人,农民,服务生只有基本工资 sal
public Worker(String name, double sal) {
super(name, sal);
}
//方法
@Override
public void printSal() {
System.out.print("工人 ");
super.printSal();//使用父类的printSal()
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework04;
public class Teacher extends Employee {//子类
//特有属性
private int classDays; //一年上课次数
private double classSal; //课时费
public Teacher(String name, double sal) {
super(name, sal);
}
//方法-重写printSal
@Override
public void printSal() { //老师不能使用super.printSal()
System.out.print("老师 ");
System.out.println(getName() + " 年工资是: "
+ (getSal() * getSalMonth() + classDays * classSal ));
}
public int getClassDays() {
return classDays;
}
public void setClassDays(int classDays) {
this.classDays = classDays;
}
public double getClassSal() {
return classSal;
}
public void setClassSal(double classSal) {
this.classSal = classSal;
}
}
- 编写Doctor类{name, age, job, gender, sal} 相应的getter()和setter()方法,5个参数的构造器,重写父类(Object)的equals()方法:public boolean equals(Object obj),并判断测试类中创建的两个对象是否相等。相等就是判断属性是否相同
package com.fyx.homework.homework07;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Doctor {
//属性
//{name, age, job, gender, sal}
private String name;
private int age;
private String job;
private char gender;
private double sal;
public Doctor(String name, int age, String job, char gender, double sal) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.gender = gender;
this.sal = sal;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
//重写父类(Object)的equals()方法:public boolean equals(Object obj),并判断测试类中创建的两个对象是否相等。相等就是判断属性是否相同
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//判断两个比较对象是否相同
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
//判断obj 是否是 Doctor类型或其子类
//过关斩将 校验方式
if (!(obj instanceof Doctor)) { //不是的话
return false;
}
//向下转型, 因为obj的运行类型是Doctor或者其子类型
Doctor doctor = (Doctor)obj;
return this.name.equals(doctor.name) && this.age == doctor.age &&
this.gender == doctor.gender && this.job.equals(doctor.job) && this.sal == doctor.sal;
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework07;
public class Homework07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试
Doctor doctor1 = new Doctor("jack", 20, "牙科医生", '男', 20000);
Doctor doctor2 = new Doctor("jack", 20, "牙科医生", '男', 20000);
System.out.println(doctor1.equals(doctor2));
}
}
- (1)做一个Student类,Student类有名称(name),性别(sex),年龄(age),学号(stu_id),做合理封装,通过构造器在创建对象时将4个属性赋值。 (2)写一个Teacher类,Teacher类有名称(name),性别(sex),年龄(age),工龄(work_age),做合理封装,通过构造器在创建对象时将4个属性赋值。 (3)抽取一个父类Person类,将共同属性和方法放到Person类 (4)学生需要有学习的方法(study),在方法里写生“我承诺,我会好好学习。”。 (5)教师需要有教学的方法(teach),在方法里写上“我承诺,我会认真教学。”。 (6)学生和教师都有玩的方法(play),学生玩的是足球,老师玩的是象棋,此方法是返回字符串的,分别返回“xx爱玩足球”和“xx爱玩象棋”(其中xx分别代表学生和老师的姓名)。因为玩的方法名称都一样,所以要求此方法定义在父类中,子类实现重写。 应当分析出,我们需要打印信息的方法, printlnfo() (7)定义多态数组,里面保存2个学生和2个教师,要求按年龄从高到低排序(8)定义方法,形参为Person类型,功能:调用学生的study或教师的
package com.fyx.homework.homework08;
public class Homework08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试老师
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("张飞", '男', 30, 5);
teacher.printInfo();
//测试学生
Student student = new Student("小明", '男', 15, "00023102");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
student.printInfo();//封装
//定义多态数组,里面保存2个学生和2个教师,要求按年龄从高到低排序
Person[] persons = new Person[4];
persons[0] = new Student("jack", '男', 10, "0001");
persons[1] = new Student("mary", '女', 20, "0002");
persons[2] = new Teacher("smith", '男', 36, 5);
persons[3] = new Teacher("scott", '男', 26, 1);
//创建对象
Homework08 homework08 = new Homework08();
homework08.bubbleSort(persons);
//输出排序后的数组
System.out.println("---排序后的数组-----");
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
System.out.println(persons[i]);
}
//遍历数组,调用test方法
System.out.println("=======================");
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {//遍历多态数组
homework08.test(persons[i]);
}
}
//定义方法,形参为Person类型,功能:调用学生的study或教师的teach方法
//分析这里会使用到向下转型和类型判断
public void test(Person p) {
if(p instanceof Student) {//p 的运行类型如果是Student
((Student) p).study();
} else if(p instanceof Teacher) {
((Teacher) p).teach();
} else {
System.out.println("do nothing...");
}
}
//方法,完成年龄从高到底排序
public void bubbleSort(Person[] persons) {
Person temp = null;
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < persons.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//判断条件, 注意这里的条件可以根据需要,变化
if(persons[j].getAge() < persons[j+1].getAge()) {
temp = persons[j];
persons[j] = persons[j + 1];
persons[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework08;
/*
抽取一个父类Person类,将共同属性和方法放到Person类
*/
public class Person {//父类
private String name;
private char gender;
private int age;
//方法
public Person(String name, char gender, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//编写一个play 方法, 把共有的输出内容写到父类
public String play() {
return name + "爱玩";
}
//返回一个基本信息
/*
姓名:张飞
年龄:30
性别:男
*/
public String basicInfo() {
return "姓名: " + name + "\n年龄: " + age + "\n性别: " + gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender=" + gender +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework08;
/*
Student类有名称(name),性别(sex),年龄(age),学号(stu_id),
做合理封装,通过构造器在创建对象时将4个属性赋值。
学生需要有学习的方法(study),在方法里写生“我承诺,我会好好学习。”
*/
public class Student extends Person{
//属性
private String stu_id;
//方法
public Student(String name, char gender, int age, String stu_id) {
super(name, gender, age);
this.stu_id = stu_id;
}
public String getStu_id() {
return stu_id;
}
public void setStu_id(String stu_id) {
this.stu_id = stu_id;
}
public void study(){
System.out.println(getName() + "承诺,我会好好学习");
}
/**
* 学生爱玩足球
* @return
*/
@Override
public String play() {
return super.play() + "足球";
}
//编写一个输出信息的方法,这样体现封装
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("学生的信息:");
System.out.println(super.basicInfo());
System.out.println("学号: " + stu_id);
study();//组合, 变化万千
System.out.println(play());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stu_id='" + stu_id + '\'' +
'}' + super.toString();
}
}
package com.fyx.homework.homework08;
/*
写一个Teacher类,Teacher类有名称(name),性别(sex),年龄(age),工龄(work_age),
做合理封装,通过构造器在创建对象时将4个属性赋值
*/
public class Teacher extends Person {
//属性
private int work_age;
//方法
public Teacher(String name, char gender, int age, int work_age) {
super(name, gender, age);
this.work_age = work_age;
}
public int getWork_age() {
return work_age;
}
public void setWork_age(int work_age) {
this.work_age = work_age;
}
//教师需要有教学的方法(teach),在方法里写上“我承诺,我会认真教学。
public void teach() {
System.out.println(getName() + "承诺,我会认真教学");
}
/**
* 老师爱玩象棋
*/
@Override
public String play() {
return super.play() + "象棋";
}
//输出信息方法
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("老师的信息:");
System.out.println(super.basicInfo());
System.out.println("工龄: " + work_age);
teach();
System.out.println(play());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Teacher{" +
"work_age=" + work_age +
'}' + super.toString();
}
}
本文章使用limfx的vscode插件快速发布