Python 培训(数据科学)numpy
说明
- numpy 和 matlab 非常像,但是用的时候总是感觉不太熟,所以相似的就不打字了,都给出例子,应该就能看懂了。
创建数组
# 1D Array
a = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
b = np.array((0, 1, 2, 3, 4))
c = np.arange(5)
d = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 5)
# MD Array,
a = np.array([[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
[26, 27, 28 ,29, 30],
[31, 32, 33, 34, 35]])
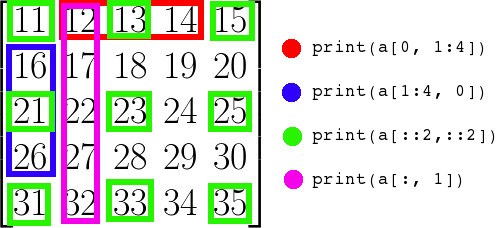
数组切片
- 切片是 Python 的切片规则
- 一维数组不能含有两个切片元素,这点也和 MATLAB 不一样
- ... 表示所有
- 切片后可能出现列向量,这时也只能用一个切片元素。
花式索引
print(a[[0, 1], [2, 3]])
- 这句话在 MATLAB 里指第 0 行和第 1 行与 第 2 列和第 3 列交叉的部分,但是在这里就只是(0,2)(1,3)两个元素
- 下面这两种则表示对应行的所有列
a[[0, 2], ...]
a[[0, 2], 1:-1:2]
数组属性
# Array properties
a = np.array([[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
[26, 27, 28 ,29, 30],
[31, 32, 33, 34, 35]])
print(type(a)) # >>><class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(a.dtype) # >>>int64
print(a.size) # >>>25
print(a.shape) # >>>(5, 5)
print(a.itemsize) # >>>8
print(a.ndim) # >>>2
print(a.nbytes) # >>>200
数组运算
# Basic Operators
a = np.arange(25)
a = a.reshape((5, 5))
b = np.array([10, 62, 1, 14, 2, 56, 79, 2, 1, 45,
4, 92, 5, 55, 63, 43, 35, 6, 53, 24,
56, 3, 56, 44, 78])
b = b.reshape((5,5))
print(a + b)
print(a - b)
print(a * b)
print(a / b)
print(a ** 2)
print(a < b) print(a > b)
print(a.dot(b))
print(a.sum())
print(a.min())
print(a.max())
print(a.cumsum())
-
普通乘除都是元素相乘相除,dot是矩阵乘法
-
含有 > 、< 返回的就是布尔矩阵
-
这里的 sum() 等是方法,上面的 size、shape 是属性
添加数组
a = np.append([1, 2, 3], [[4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
b = np.append([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [7, 8, 9], axis=0)
# a为一维数组,b为二维数组
- 特别注意,输入参数数组本身不会不变,要返回一个参数
逻辑筛选
- 逻辑筛选和MATLAB一样,本质都是先生成一个逻辑数组,生成逻辑数组方法除了 > 等符号外,还有 numpy 中的函数,比如 isreal
- 逻辑数组之间的逻辑运算也是用 numpy 中的函数,logical_and、logical_or、logical_xor、logical_not
- 筛选和 MATLAB 一样,放在索引里
import numpy as np
b = a[a > 5]
mark = np.logical_and(a >= 5, a <= 10)
c = a[mark]
函数文档
- numpy 的中文API文档:https://www.numpy.org.cn/reference/routines/
- 需要什么函数就可以去查了
本文章使用limfx的vsocde插件快速发布